cayenne: a Python package for stochastic simulations
cayenne is a Python package for stochastic simulations. It offers a simple API to define models, perform stochastic simulations with them and visualize the results in a convenient manner.

Install
Install with pip:
$ pip install cayenneDocumentation
- General: https://cayenne.readthedocs.io
- Benchmark repository, comparing
cayennewith other stochastic simulation packages: https://github.com/Heuro-labs/cayenne-benchmarks
Usage
A short summary follows, but a more detailed tutorial can be found here. You can define a model as a Python string (or a text file, see docs). The format of this string is loosely based on the excellent antimony library, which is used behind the scenes by cayenne.
from cayenne.simulation import Simulation
model_str = """
const compartment comp1;
comp1 = 1.0; # volume of compartment
r1: A => B; k1;
r2: B => C; k2;
k1 = 0.11;
k2 = 0.1;
chem_flag = false;
A = 100;
B = 0;
C = 0;
"""
sim = Simulation.load_model(model_str, "ModelString")
# Run the simulation
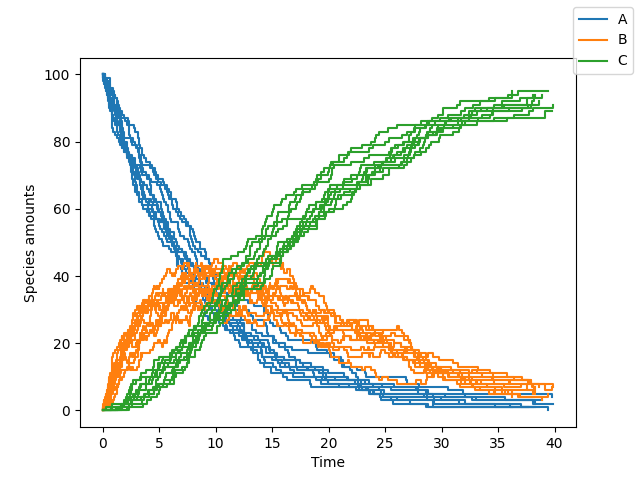
sim.simulate(max_t=40, max_iter=1000, n_rep=10)
sim.plot()
Change simulation algorithm
You can change the algorithm used to perform the simulation by changing the algorithm parameter (one of "direct", "tau_leaping" or "tau_adaptive")
sim.simulate(max_t=150, max_iter=1000, n_rep=10, algorithm="tau_leaping")Our benchmarks are summarized below, and show direct to be a good starting point. tau_leaping offers greater speed but needs specification and tuning of the tau hyperparameter. The tau_adaptive is less accurate and a work in progress.
Run simulations in parallel
You can run the simulations on multiple cores by specifying the n_procs parameter
sim.simulate(max_t=150, max_iter=1000, n_rep=10, n_procs=4)Accessing simulation results
You can access all the results or the results for a specific list of species
# Get all the results
results = sim.results
# Get results only for one or more species
results.get_species(["A", "C"])You can also access the final states of all the simulation runs by
# Get results at the simulation endpoints
final_times, final_states = results.finalAdditionally, you can access the state a particular time point of interest $t$. cayenne will interpolate the value from nearby time points to give an accurate estimate.
# Get results at timepoint "t"
t = 10.0
states = results.get_state(t) # returns a list of numpy arraysBenchmarks
| direct | tau_leaping | tau_adaptive | |
|---|---|---|---|
| cayenne | :heavy_check_mark: Most accurate yet | :heavy_check_mark: Very fast but may need manual tuning | Less accurate than GillespieSSA’s version |
| Tellurium | :exclamation: Inaccurate for 2nd order | N/A | N/A |
| GillespieSSA | Very slow | :exclamation: Inaccurate for initial zero counts | :exclamation: Inaccurate for initial zero counts |
| BioSimulator.jl | :exclamation: Inaccurate interpolation | :exclamation: Inaccurate for initial zero counts | :exclamation: Inaccurate for initial zero counts |
License
Copyright (c) 2018-2020, Dileep Kishore, Srikiran Chandrasekaran. Released under: Apache Software License 2.0
Credits
- Cython
- antimony
- pytest
- Cookiecutter
- audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage
- black
- Logo made with logomakr
